Overview
This dataset provides in-situ surface observations archived by the Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC). It containes data from the MSC operational observation system as well as from their parteners. Therefore, not all stations are QC or maintained by MSC. The network of stations containes stations with only automatic instruments, and human observing (or manual) stations.
Provider's contact information
Environment and Climate Change Canada
donneesclimatiquesenligne-climatedataonline@ec.gc.ca
Licensing
Open Government Licence - Canada.
Variable name and units:
Direction of Maximum Gust (10s deg)
Speed of Maximum Gust (km/h)
Hourly wind speed/direction (km/h)
Spatial coverage and resolution:
Canada, point locations.
Temporal coverage and resolution:
Time period varies per station with data for in the North starting in 1940’s or 1950’s until present.
The data is available at the hourly, daily and monthly time step.
- Hourly: indicates data values for observations taken on an hourly basis.
- Daily: indicates data values for observations taken once in a 24-hour period or derived from hourly data values.
- Monthly: are totals for each month, derived from daily data values.
The data will continue to be updated regularly.
Information about observations (number, homogeneity)
The number of active stations changed over time. The following figure from Mekis et al. (2018) is presenting the locations of the surface weather stations across Canada with a Needs Index map in the background as of September 2016.
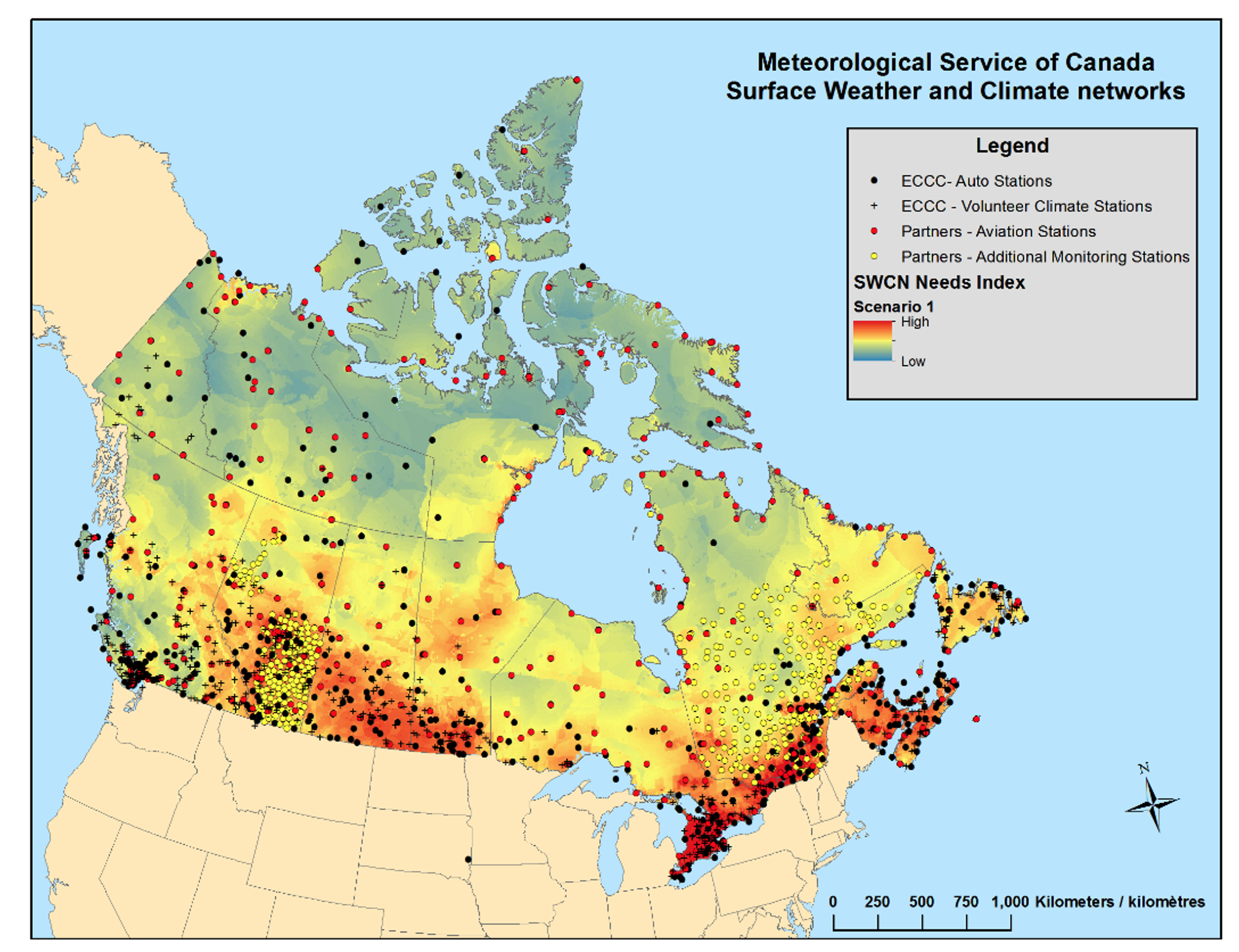
Figure 1. Surface weather stations across Canada, as of September 2016, with a Needs Index map in the background. For further details on station network evolution see Mekis et al. 2018. [Source: Mekis et al., 2018].
Stations over Northern Canda with wind measurements are the ECCC atomatic stations and stations from the Aviation Monitoring Station network (which include automated and staffed weather stations) operated by NAV CANADA and the Department of National Defence (DND). The ECCC Volunteer Climate Stations provide just temperature and precipitation measurements.
Methodology
Raw and quality-controlled station observations are archived and managed by the MSC’s Archive Operations and Climate Services. Observations from different instruments are stored in different formats in the national archive. The methodology, the instruments and the location of instruments have changed in time. Many of initialy manual stations were replaced with automatic stations. The following is summarising some information regarding the manual measurements that should be considered when using historic station data.
Wind speed is usually observed at 10 metres above the ground. It represents the average speed during the one- or two-minute period ending at the time of observation for aviation station. For Aviation Weather Reports, a one-minute mean of wind direction and speed was used until the late 1980s. The wind speed now represents the average speed during the two-minute period ending at the time of observation, for Aviation stations. The only historical 10-minute mean wind data are winds from the synoptic reports. Synoptic reports are only created four times a day: 12z, 18z, 00z, 06z.
Some stations are equipped with a standard type U2A anemometer, taking one minute or (since 1985) two-minute mean speeds values at each observation. At other wind-measuring sites, values are usually obtained from autographic records of U2A or 45B anemometers. Averaging periods at these sites may vary from one minute to an hour. The current standard at automated stations is the RM Young.
In observing, wind speed is measured in nautical miles per hour and converted to kilometres per hour. The extreme gust speed is the instantaneous peak wind observed from the anemometer dials, or abstracted from a continuous chart recording. A value of zero (0) denotes a calm or no wind.
Conversion factors: 1 nautical mile = 1852 m or 1.852 km
Therefore: 1 knot = 1.852 km/h and 1 km/h = 0.54 knot.
Wind directions measured by U2A's are recorded to the nearest ten degrees, while those from the 45B are provided to 8 points of the compass. All wind directions are defined as the direction from which the wind blows with respect to true or geographic north. For example, an easterly wind is blowing from the east, not toward the east. A wind direction observation represents the average direction over the two-minute period ending at the time of observation. Certain sites measure only the wind. The daily climate sites typically don’t measure the wind.
Information about the technical and scientific quality
This dataset represents Environment and Climate Change Canada’s official station observations. Data are subject to change on an on-going basis as MSC is constantly QCing the data from ECCC stations. Not all data has the same level of QA/QC (i.e. aviation dat is not QA/QC by MSC but by NAV CANADA).
Limitations and strengths for application in North Canada
It is a challenge to sustain a cost-effective observing system over Norther Canada because of a large part of the teritory is constituted by remote areas (it is hard for technicians to fly to the site for maintenance, and they often have to wait for the thaw). The special climatic conditions produce a large risk of power and telecommunication outages, and anemometer to freeze due to cold temperature or freezing rain. Concequently, observations in Nortehrn Canada are sparse and records are often incomplete.
References to documents describing the methodology or/and the dataset
The manual specific for aviation observations/reports (MANOBS): http://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2019/eccc/En56-238-2-2018-eng.pdf and http://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2019/eccc/En56-238-2-2018-fra.pdf
https://climate.weather.gc.ca/doc/Technical_Documentation.pdf
Link to download the data and format of data:
Hourly, Daily and Monthly
Database searchable by location for CSV via CDO/MSC/ECCC: https://climate.weather.gc.ca/historical_data/search_historic_data_e.html
Only Hourly:
Map based extraction tool for GeoJSON and CSV on CCCS/ECCC: https://climate-change.canada.ca/climate-data/#/hourly-climate-data
Note: Only a subset of the total stations is shown due to size limitations. The priorities for inclusion are as follows: (1) Station is currently operational, (2) Stations with long periods of record, (3) Stations that are co-located with the categories above and supplement the period of record. For additional stations not included, go to CDO/MSC/ECCC.
Only Daily
Map based extraction tool for GeoJSON and CSV on CCCS/ECCC: https://climate-change.canada.ca/climate-data/#/daily-climate-data
CSV via MSC/ECCC: https://dd.weather.gc.ca/climate/observations/daily/
Note: Only a subset of the total stations is shown due to size limitations. The priorities for inclusion are as follows: (1) Station is currently operational, (2) Stations with long periods of record, (3) Stations that are co-located with the categories above and supplement the period of record. For additional stations not included, go to CDO/MSC/ECCC.
Only Monthly
Map based extraction tool for GeoJSON and CSV on CCCS/ECCC: https://climate-change.canada.ca/climate-data/#/monthly-climate-summaries
CSV via MSC: https://dd.weather.gc.ca/climate/observations/monthly/
Publications including dataset evaluation or comparison with other data in northern Canada
There are no publications that evaluate station data specifically on northern Canada. The following papers are providing general discussions on the issues with wind records at stations in Canada for climate analysis.
Wan, H., X. L. Wang, V. R. Swail, 2010: Homogenization and trend analysis of Canadian near-surface wind speeds. Journal of Climate. 23, 1209-1225.